TL;DR: This article delves into the profound impact of AI advancements on daily life and the realms of business and marketing. It explores how the next wave of generative AI will redefine consumer technology and business operations. We also examine the transformative potential of generative AI in various aspects of marketing, such as strategy, content creation, search, customer relationship management, and social media.
- The profound impact of AI on daily life and business
- Living with GenAI: conversational services, personal assistants, dynamic experiences, and AI hardware
- Working with GenAI: cognitive business processes, AI-driven strategy, and customized product design
- Generative AI in marketing: strategy, content, search, CRM, and social media
- The importance of building for the present while planning for the future
Following the bright flash of rapid advancements in artificial intelligence, we’re now bracing for the thunderclap—the dramatic changes that will reverberate through our daily lives and the realms of business and marketing. This section looks at the likely developments we will witness as we move forward.
Living with GenAI
The next wave of GenAI promises to redefine consumer technology with capabilities far beyond our current expectations. Here’s what we are beginning to see:
- Conversational Businesses/Services
Emerging AI solutions that understand and respond to human language with unprecedented sophistication. Google, OpenAI, and Moshi’s latest developments are showing early signs of systems that can engage in free-flowing conversations and are capable of assisting with a wide array of tasks. With developments such as Grok’s inference chip, the speed and cost efficiency of the response will allow conversations with AI that are indistinguishable from humans. As well as Grok, we have also seen the rapid response of AI happening within the latest iteration of OpenAI’s GPT-4o, powering the voice assistant and enabling real-time communication with the assistant. This development opens remarkable opportunities for how we engage with technology, making interactions more natural and intuitive than ever before. - Intuitive Personal Assistants
Generative AI is set to empower personal assistants (alternatively referred to as agents) to manage our lives for us. Managing our diaries, liaising with people on our behalf, advising and guiding us. What was set out as a long-term potential in Sentience, PHD’s 2015 project on the future of AI, is now only two or three years away. As well as organizing our lives, they will make decisions for us. In essence, they will be decision-makers on the choice of brand/service. And with that, they will become a target audience, focusing on how to influence the decisioning algorithm (of an emergent LLM). User reviews and sentiment will be an increased area of focus for organizations. As LLMs become more efficient, we will soon see personal agents hosted locally on our smartphones. Think of augmented versions of Siri with Apple’s announcement of ‘Apple Intelligence.’ Uniquely tailored to and knowledgeable about the user, Personal Agents will be able to chain actions in a sequence, supporting everything from daily tasks such as organizing schedules to researching and negotiating big-ticket purchases. Within a few years, conventional search and website traffic could see a significant impact as agents connect directly to other agents with no human oversight. - Dynamic Experiences
The next phase in interface design will be shaped by AI that anticipates user needs. Interfaces that adapt in real-time provide a truly personalized experience by learning from your habits and preferences. The combination of technologies such as OpenAI’s Sora and Google’s Genie—as covered in Lightning—will enable truly dynamic and fluid experiences tailored specifically to the interest and intent of the experience. It is likely to be adopted by brands, where, for example, the browser experience is bespoke to the individual using it (subject to their consent to share their data). It also opens the opportunity for media experiences tailored to the individual. For example, a rolling 24-hour news platform tailored specifically to the individual—where the presenter, the topics covered, and the video content are all generated dynamically from API feeds, modified with RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) so that it is relevant to the viewer. - GenAI Hardware
With AI working at the hardware level, pioneered by Microsoft with UFO (UI Focused Agent)—which they referred to as ‘an agent for Windows interaction’ – expect to talk to your laptop. Imagine speaking naturally to any piece of hardware, be it your car or a kitchen appliance, and being understood. Much of what surrounds us is ‘conversational’ – transforming our interaction with technology. - Conversational AI within Search: The Start-to-Stop Search Experience
As new search formats like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and Perplexity (a generative search engine) allow consumers to convey ideas in natural language, upload images or videos as a reference, ask follow-up questions, and even buy products- search will gain more traction across the entire consumer journey, acting as a source of inspiration beyond more functional search inquiry. Brands need to optimize their search strategies to ensure priority content and messaging appear in the aggregated output of these new formats. - Conversational AI in Ambient Products
Conversational AI is re-invigorating the field of in-home smart devices such as Alexa. As companies like Amazon upgrade the capabilities of Voice Assistants with more advanced LLMs, the scope of use will expand from setting timers and switching on lights to conversational search, personalized product recommendations, and purchases. - Conversational AI in Ad Units: The Brand Concierge
A wave of new tools and services that humanize brand interaction beyond the chatbots we currently use is coming to market. Hyper-realistic video avatars customized to brand tone, along with multimodal chatbots capable of low-latency generative audio and image creation, are set to provide a more personalized, engaging sales experience. Trained on the brand product portfolio, they also offer increasing control of conversational flow to drive better business outcomes.
The goal of Ascension is to elevate tangible solutions that are ready and can make a difference to clients’ businesses but to do it in a way that helps perhaps demystify some of the buzz and the chatter in the industry.
Guy Marks, CEO
PHD Worldwide
Working with GenAI
The incorporation of generative AI into business realms is poised to transcend traditional automation, offering nuanced, intelligent, and creative problem-solving that mirrors human thought processes.
With the release of OpenAI’s ChatGPT-4o and its desktop application, the AI will be able to watch you as you work, and you can ask questions about it as you are working. For example, you could ask, “What is this bar chart really telling me? What information do you have about this that could help?” This passive viewing of the work that you are doing would allow the AI to operate as a true co-pilot, irrespective of the discipline and area of work that you are engaged in.
As these technologies mature, here’s what we anticipate in the business sector:
- Cognitive Business Processes
Enterprises are starting to develop AI systems that can understand and execute business tasks independently. This includes platforms like OpenAI’s Codex, which can write and review code, potentially revolutionizing software development by automating more functional tasks. - AI-Driven Strategy Formulation
Business strategy is another area ripe for disruption. Generative AI, through predictive modeling and scenario generation, will soon inform strategic decisions, providing a range of potential outcomes based on economic indicators, market trends, and consumer behavior analyses. - Customized Product Design
Generative AI can increasingly consider consumer feedback and market data to suggest design modifications or entirely new products, significantly speeding up the R&D process.
Boom: Emerging From the Lab Into the World
Generative AI-based tools and capabilities continue to be launched at an unprecedented rate. Here’s a taste of some of the most recent – this list is created generatively, so check back regularly for the latest from the world’s AI labs.
- Latitude.io: Provides AI-generated gaming experiences with its flagship product, AI Dungeon, which allows users to interact with AI-driven narratives.
- Character.AI: Offers a platform for creating and chatting with user-generated characters, useful for entertainment and simulating conversations.
- Hugging Face: A collaborative AI community providing tools for developers, including over 61,000 pre-trained models and 7,000 datasets.
- AssemblyAI: Offers AI-as-a-service with APIs for automated speech transcription and content moderation across 80 languages.
- Promptbase: A marketplace for buying and selling AI prompts to generate predictive results using popular AI tools.
- Rephrase.ai: Simplifies video production by converting text into professional-looking videos with digital avatars, serving a wide range of users.
- Sudowrite: A writing assistant designed to support authors and content creators by enhancing their creative processes.
- Quizgecko: Provides AI-powered educational evaluation services, allowing institutions to conduct tests and exams with instant assessment features.
- Writesonic: Helps businesses create SEO-optimized content that aligns with their brand voice, catering to organic marketing needs.
- TalkPal: Offers language learning support using generative AI, providing personalized lessons in 57 languages.
- Moonvalley: A promising startup for text-to-video creation, currently in beta, known for producing animations and realistic videos.
- Humata AI: Provides a tool for document management, allowing users to ask questions and receive answers about specific documents, enhancing efficiency.
- Hippocratic AI: Focuses on integrating generative AI into the medical field, aiming to improve healthcare solutions with AI technology.
- Grok AI: All-rounder LLM, text and text-to-image (powered by FLUX) image generator which has faced criticism due to lack of safeguards.
- Meta’s AI Studio: Designed for Instagram creators and business owners, AI Studio allows users to create custom AI chatbots with personalized traits to engage more effectively with followers. By leveraging Meta’s Llama 3.1 model, it provides sophisticated interactions and auto-reply features, enhancing customer engagement and brand presence across Instagram, Messenger, and WhatsApp.
- Luma AI’s Dream Machine 1.5: This text-to-video generation tool offers enhanced realism and improved understanding of prompts, including non-English content, making it valuable for marketers and agencies creating multilingual and dynamic video content. Its “Extend Video” feature supports longer clips, broadening creative possibilities for marketing campaigns. (Available in both free and paid tiers)
- Adobe Firefly Image 3: Integrated into Adobe Creative Cloud, Firefly Image 3 offers auto-stylization and photorealistic rendering capabilities, ideal for generating diverse visual content for digital marketing. With seamless integration into Adobe apps like Photoshop and InDesign, it streamlines workflows for creating compelling marketing materials while ensuring compliance with intellectual property rights.
- Prompt AI: Focuses on democratizing access to advanced computer vision technologies using large language models. It aims to make computer vision accessible to everyday users, empowering them to solve impactful problems related to personal media.
- Inworld AI: It’s revolutionizing the gaming industry by integrating AI-powered characters into video games. The startup has raised significant funding to develop generative characters that mimic human behaviors and enhance player engagement.
- Jasper AI: Originally an AI writing assistant, Jasper AI has evolved into a comprehensive content creation platform. It leverages advanced generative AI models to assist businesses in scaling their marketing content across various formats.
- Tome: A productivity tool that allows users to create visually stunning presentations with ease, making it accessible for those without graphic design experience.
Working with GenAI in Marketing
The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence have sent shockwaves through industries around the world. While AI has been driving transformation through analytics, automation, and decision support for years, the recent breakthroughs in generative AI models like Claude, GPT-4, Midjourney, Sora, and Kling have opened even more profound possibilities that are reverberating across sectors and marketing in an industry at the forefront of development – and disruption. This, according to Jevon’s Paradox (see below), may lead to an increase in the size of the industry.
The Jevons Paradox and Marketing
The Jevons Paradox, originally observed by William Stanley Jevons in the 19th century, highlights an intriguing counterintuitive dynamic: improvements in resource efficiency often lead to increased, not decreased, consumption of that resource. Originally noted in coal consumption, the paradox has surfaced in various sectors, from energy-efficient lighting leading to more widespread use of lights to fuel-efficient cars prompting more travel.
Applying this concept to the marketing services industry, with the advent of Al, reveals potential transformative shifts. Any increases in efficiency will allow existing advertisers to invest in previously unaffordable but needed marketing capabilities.
For most advertisers, a positive profit-ROl can be achieved through hiring in new capabilities – so those that reinvest will typically outpace those that don’t. Simultaneously, it opens the door for smaller companies and start-ups, which were once priced out, to enlist professional marketing services.
The likely outcome for agencies will be a broadening of their service offerings to cater to this diversified clientele. Expect to see a proliferation of more specialized services and perhaps a shift towards leaner service models where Al handles routine tasks, facilitating a long tail of smaller yet highly engaged clients.
The profound developments in generative AI are not just reshaping our daily work experiences—they’re setting the stage for a radical transformation in how brands connect with customers. Powered by large language models and multimedia generation capabilities, AI is becoming a driving force for unprecedented levels of personalization, creativity, and real-time engagement in marketing.
Generative Strategy
As enterprises centralize their data into AI clouds, a new wave of strategy development will emerge—embedding generative AI and cognitive assistants into the planning processes. AI can become an indispensable strategic co-pilot by training large language models on an organization’s unified data estate of market research, sales data, customer feedback, competitor analysis, and more:
Guy Marks, CEO, PHD Worldwide – Interviewed June 2024
- Rapid Situation Assessment: Rather than months of upfront desk research and data wrangling, cognitive assistants can ingest and synthesize an enterprise’s collective knowledge in minutes. They can then provide concise situational assessments like market landscapes, trend overviews, channel performance analysis, and more at the marketing strategist’s query. This accelerates the crucial “understanding the context” phase of strategic development.
- Insight Extraction and Ideation: Beyond situational inputs, AI assistants can also derive elevated insights by processing disparate data signals that may not have been previously connected by human strategists alone. These AI-surfaced insights around customer needs, market white spaces, emerging behaviors, and more can catalyze breakthrough brand positioning, creative campaign ideas, and innovative go-to-market approaches.
- What-If Scenario Modeling: As campaign ideas take shape, cognitive assistants can then leverage their broad knowledge models to pressure-test strategies through probabilistic simulations and what-if scenario modeling. The AI can project potential impacts across multiple dimensions like sales forecasts, brand health tracking, channel ROI performance, and more. This allows iterating and refining game plans before costlier execution phases.
- Embedding AI into Workflows: Many brands and agencies are taking this paradigm shift even further by embedding generative AI directly into campaign development workflow platforms like Omnicom’s Omni. These tools use engineered prompts to give strategists and creatives an AI cognitive companion. As users move through the workflow platforms, the integrated AI can proactively:
-
-
- Conduct supplemental desk research and insight gathering.
- Surface relevant case studies and best practice examples.
- Ideate multiple creative concept directions.
- Prototype execution tactics and resource estimates.
- Forecast and optimize projected performance.
-
This seamless human-AI collaboration allows faster iteration and smarter exploration of the entire integrated marketing strategy space before finalizing directions.
From empowering a new level of data-driven brand navigation to accelerating creative processes, generative AI will fundamentally reshape how strategies are crafted and campaigns developed.
Generative Content
Generative AI is empowering content creators and marketers at every stage of the production process. It begins with tools like Midjourney and Runway, which can generate preliminary designs, storyboards, and films simply from text descriptions. This allows creative teams to rapidly explore many different visual directions before committing resources.
Once an overall creative vision is established, generative AI will play an increasingly pivotal role in developing the final polished assets and experiences.
Caroline Yap, Managing Director, Global AI Business and Applied Engineering, Google – Interviewed June 2024
Including the uploading of 3D-rendered assets like products, environments, and branded elements into AI platforms like Adobe Substance 3D and Nvidia Omniverse, among others.
Using natural language prompts, these AI tools can then manipulate and iterate on the 3D assets, seamlessly adjusting materials, lighting, and compositions and introducing new objects. This allows for incredibly fast prototyping and experimentation.
For example, a developer could upload a 3D render of a car into an AI environment, then use text prompts such as “make it a cyberpunk-themed hot rod” or “place it in a photorealistic Tokyo cityscape at night” to completely transform the look and scene around the vehicle.
Source: runwayml, X (Formerly Twitter)
Frontier Text-to-Video platforms are now enabling capabilities in video production that were previously unattainable or prohibitively expensive for most commercial budgets. One notable example is the seamless transition and/or morphing between objects. This remarkable creative capability is another area currently being explored and developed by marketers and agencies.
Looking ahead, these AI-generated marketing assets and experiences will eventually evolve and customize themselves in real time based on individual audience signals and data passed from ad servers.
The boundaries between creative ideation, content production, and personalized delivery will blur.
Generative Social
Generative AI’s ability to create engaging content at scale, enable real-time personalized interactions, and unlock new creative powers for influencers and creators will profoundly reshape the social media landscape.
For social media marketers tasked with feeding the insatiable content demands of multiple platforms, generative AI has become a powerful aid. AI tools can rapidly generate on-brand visual assets like images, GIFs, and short video clips based on text prompts aligned with campaign creative briefs. Written captions, hashtags, and even audio/voice snippets for videos can also be AI-generated.
This will increasingly allow a high volume of channel-optimized social media posts and ads at a fraction of the previous production workload. As real-time trends and cultural moments unfold, AI will ensure brands can capitalize quickly with reactive content.
The rise of AI image generation has also opened new creative vistas for social media influencers and creators. Rather than just sharing conventional photo/video shoots, they can now co-create with AI to produce highly stylized, digitally unique visuals and animated works that stand out in feeds. This will continue to democratize abilities previously limited to seasoned digital artists and creators.
Creators and Influencers
The rise of generative AI is empowering Creators to become self-sufficient “one-person studios.” These tools are removing traditional barriers to entry, allowing individuals to direct, produce, and distribute high-quality multimedia content without needing large teams or extensive resources. This shift fosters a more diverse Creator landscape, representing a wider range of voices and perspectives.
Building on this trend, the digital landscape is witnessing a transformation with the rise of virtual influencers and AI-enhanced engagement strategies. AI-generated entities like Eternity, an 11-member K-pop group, are gaining traction on social media, each member crafted with unique characteristics to appeal to a global audience. This trend extends to the music industry, with virtual singers like Noonoouri, signed by Warner Music, utilizing generative AI for music creation and brand promotions.
Simultaneously, platforms like DreamGF are digitalizing real-life models and influencers, creating AI versions capable of lifelike interactions. This technology enables continuous engagement, as demonstrated by Twitch streamer Amouranth, who employs an AI version of herself to respond to fans in her own AI-generated voice.
Beyond virtual personas, generative AI is revolutionizing influencer operations. It assists with data analytics, brand collaboration matching, scheduling, and administrative tasks, streamlining the workflow for self-employed content creators.
This technological integration is helping influencers manage their overwhelming fan interactions more efficiently, while also enhancing their content strategy and business operations.
Generative Search (and RMNs)
With generative AI language models like Claude and ChatGPT being used to answer questions that were typically put to traditional search engines, brands must rethink their approach to SEO.
Brands are already exploring how to develop website content, product data, and branded messaging optimized for how large language models will interpret and represent the brand when generating natural language search results. Getting this right is crucial to ensure that the brand appears within the LLM’s response and with the correct framing.
This monumental shift for SEO preceded the integration of generative AI into the core search experiences on major platforms like Google and Bing. As LLMs become more embedded into the delivery of existing search results, new paid search opportunities will open.
Google’s rollout of Search Generative Experiences (SGE) integrates AI-derived results into search engine results pages (SERPs), potentially impacting a significant portion of queries. SEO tech providers suggest that up to 84% of all queries could include SGE. This shift may have profound implications for Google’s search advertising revenue and downstream effects on websites and brands.
Meanwhile, Perplexity AI, a startup search engine, is gaining traction by offering direct AI-generated answers and citations. This approach presents a novel approach to information retrieval that could further disrupt traditional search paradigms and user expectations.
While SGE presents both opportunities and threats, brands must adapt to ensure visibility in SGE results and develop strategies to mitigate changes in search behavior and traffic share across search tactics.
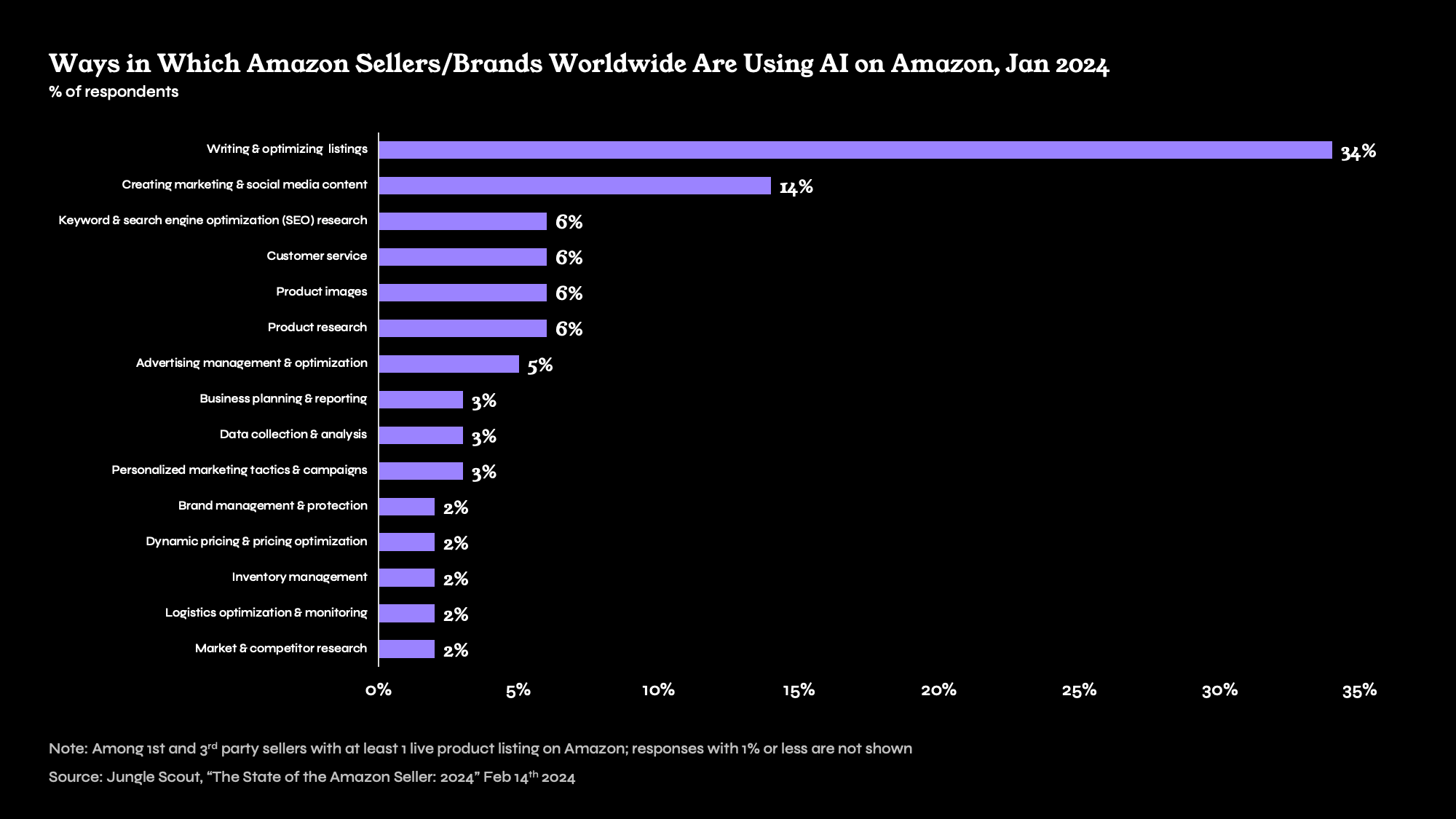
In parallel, there will continue to be further developments in how search planners can leverage the intelligence of LLMs to inform keyword strategies, messaging, content, and new product development. Specifically, within Retail Media Networks—a study by Jungle Scout published by eMarketer in the first half of 2024 indicated that 34% of Amazon sellers worldwide are already using GenAI to write and optimize listings.
Generative E-commerce
In terms of commerce marketing, more broadly, AI will largely be used to find product and price market fit in fast-moving, iterative production pipelines.
However, if you consider commerce platforms and sectors with longer fulfillment timelines, the possibility emerges of marketing products that do not yet exist: production on demand. This is a less wasteful fulfillment pipeline than many existing e-commerce solutions, and we would expect it to be adopted more broadly across some categories as this competitive advantage is realized.
Leading the charge in this AI-driven e-commerce revolution is Amazon, which is actively deploying generative AI across its platform to enhance the customer experience. The company has launched Rufus, an AI-powered shopping assistant that can answer questions, offer product comparisons, and make suggestions for Amazon app users. Additionally, Amazon is developing dozens of other generative AI-powered applications to improve personalization, streamline product listings, and revolutionize various aspects of the shopping journey. These innovations not only aim to increase sales and customer satisfaction but also have the potential to reshape the entire e-commerce landscape, setting new standards for personalized shopping experiences and efficient inventory management.
Generative CRM
Generative AI is ushering in a new era of customer relationship management by turbocharging personalization, automating service workflows, and unlocking customer insights. At the heart of this transformation are large language models that can understand and generate human-like responses across multiple conversational modes—text, voice, and visuals.
One of the biggest impacts of generative AI on CRM will be enabling next-generation personalized communication and service at an unprecedented scale. AI assistants will handle customer requests via chat, email, or voice with personalized and contextual responses that continue conversational threads naturally.
Whether it’s providing tailored product recommendations, guiding customers through self-service workflows, or resolving common issues, generative AI will deliver high-touch experiences even for businesses with millions of customers. With the involvement of human agents to focus on more complex situations flagged by the AI.
Generative AI will also revolutionize traditional marketing automation. Rather than sending generic, templated campaigns, brands will leverage AI to dynamically generate the actual content.
Powering these personalized engagement capabilities is generative AI’s unique ability to rapidly analyze and generate insights from siloed and unstructured data across an organization. CRM systems, customer surveys, support transcripts, public reviews, contextual buying data, and more can all be ingested and synthesized by AI models, with the model optimized for LTV (Lifetime Value).
Salesforce is integrating generative AI into its CRM platform through Einstein GPT, which can create personalized content across sales, service, marketing, and IT interactions. This AI technology generates tailored emails, marketing content, and even code while leveraging real-time data from Salesforce Data Cloud to ensure relevance. Additionally, Salesforce has partnered with OpenAI and developed an AI benchmark for CRM, aiming to enhance customer experiences, improve productivity, and revolutionize how businesses manage customer relationships.
Blockchain and AI
Whilst the conversation around Web3 has been somewhat surpassed by Al, these technologies may come to solve some of the issues that surfaced by the widespread adoption of Al in marketing.
Blockchain can provide a layer of security. Assets generated or hosted in a brand-controlled on-chain environment can prove true provenance, they are transparent and immutable. A scenario in which every legitimate brand or organization-generated asset has a watermark that can be scanned to see the on-chain records of that asset.
The Impact of AI on Media Buying
Machine learning has already disrupted media buying. Over the last few years, the trading platforms used for programmatic buying, known as Demand-Side Platforms (DSPs), have integrated machine learning algorithms to optimize bid factors applied to target audiences. Agencies have advanced this further by replacing standard algorithms with bespoke ones, often referred to as BYOA (Bring Your Own Algorithm). This allows for the creation of custom machine-learning algorithms that can utilize existing target audiences, often derived from first-party data with consent, for programmatic buying purposes.
In this setup, the algorithm can access the bid stream, often processing more than 50,000 impressions per second. It can identify a device ID within the bid stream that matches the target audience list and then set the bid price for that individual device ID. If the bid is successful, the ad is served to the targeted device, showcasing the power of machine learning already deployed in media buying.
Looking forward, there is an opportunity to use generative AI to enhance this process. Generative AI can incorporate unstructured data, such as information about the device ID, to make more sophisticated judgments on bid prices. Additionally, generative AI can enhance media planning by enabling micro-decision planning. It can consider factors like the context of the environment, the sequence of messaging, and the time of day, utilizing a vast amount of unstructured data to determine the optimal approach. This operates as a deep learning algorithm, surpassing the capabilities of traditional machine learning.
However, human intervention is still crucial. Setting up the model requires various data sets and the construction and connection of technology. Human oversight is necessary to observe, refine, and adjust the model, as well as to interpret the results for clients. This elevates the role of individuals, allowing them to leverage technology to rise above routine tasks, much like previous technological advancements have done.
Generative Modeling – Using Synthetic Data to Simulate Markets
Researchers Peiyao Li, Noah Castelo, Zsolt Katona, and Miklos Sarvary from the Haas School of Business at the University of California, Berkeley, and the Alberta and Columbia Business Schools have highlighted the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) for market research.
Sean Betts, Chief Product & Technology Officer, OMG UK – Interviewed June 2024
Their studies demonstrate LLMs’ ability to substitute human participants, achieving agreement rates over 75% across various product categories and even up to 90% in perceptual maps of car brands. This indicates that LLMs can effectively replicate human responses, offering significant efficiencies in research processes by reducing time and costs.
LLM for Primary Research
To assess the predictive accuracy of LLMs, PHD carried out a series of tests – comparing the predictions of Claude 3 and ChatGPT 4o. ChatGPT was the most effective at predicting metrics without seeing the data. It achieved an average accuracy level of 70.1% across the studied markets, as shown in the table below. Interestingly, the accuracy for China was only 38.7%, indicating that the LLMs may have limitations in accessing and analyzing data from Chinese walled-garden platforms.
| LLM for Brand Research | Chat GPT4o Vs Primary Research for Luxury Brand Across Asia | |||
| Metric | Average Prediction Accuracy | ||
| Unaided Brand Awareness | 50.9% | ||
| Aided Awareness | 87.6% | ||
| Consideration | 75.4% | ||
| Purchase Intent | 66.7% | ||
| Average % Accuracy | 70.1% | ||
Source: PHD May 2024. Across: Australia, Japan, China, South Korea, Singapore and Malaysia. Note: China prediction accuracy is only 38.9%
This analysis underscores the remarkable power of using LLMs – in particular, ChatGPT4o – to carry out research. It also highlights the ability to ask questions that are hard to address in real life, namely defining and sizing the need states that drive category purchases (research that is very hard and expensive to do).
LLMs are particularly useful in generating synthetic data for nuanced market analyses. They can handle demographic variations and contextual differences that are typically challenging for traditional research methods. This technology is ideal for creating perceptual maps, evaluating brand similarity, and assessing consumer preferences, revolutionizing how market insights are gathered and analyzed in the marketing field. But it brings into question appropriate data usage and, with that, an understanding of data regulation – see below.
Early Regulation Emerges
In response to this and other ethical questions, the European Union passed the Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act) in March 2024. This landmark legislation established the world’s first comprehensive framework for AI, with implications for marketers across Europe and beyond.
Transparency is a key pillar of the Act. Marketers must clearly inform consumers when interacting with AI, such as chatbots used for customer service. Data privacy also takes center stage, with the Act tightening regulations on data collection and user consent, especially for AI-powered personalization and targeted advertising. Marketers may need to find alternative methods that rely less on sensitive data segments.
The early regulation presents a chance for marketers to prioritize responsible AI practices, such as avoiding algorithm bias and ensuring clear communication. In doing so, marketers can build stronger relationships with consumers, and in the long run, this can lead to more effective and ethical marketing strategies that resonate better with a privacy-conscious and aware audience.
Summary
As enterprises continue to embrace generative AI across their marketing functions, the weight of AI’s impact on shaping strategies and creative execution will only continue growing, redefining the entire industry’s workflow and unlocking new frontiers of performance.
The danger is to be a passenger to the change – to be waiting for the platforms to merge.
Realizing AI’s transformative potential requires a deliberate, structured approach within organizations. Implementing ad-hoc AI point solutions is inadequate; companies must have a cohesive AI strategy that maps to their core marketing and business objectives.
For organizations that are now investing in generative AI across their business, it is important to understand what can be done today while planning for tomorrow. Because of the speed of development, failure to do this will lead to organizations making a leap but then being leapfrogged by their competitors.
We need to understand what we should be building now and what we should plan for tomorrow.
To answer that, we must project how AI will evolve over the next few years leading up to 2030. That is the focus of the three articles covering these Winds of change. From the current period of experimentation (2024-2026), through an era of acceleration (2026-2028), to an ultimate place of elevation (2028-2030) in which marketing is fundamentally and irreversibly transformed.